Key Takeaways:
- GEO makes brands visible in AI-generated answers – such as ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Mode, or Google Gemini.
- GEO ≠ SEO: GEO complements traditional SEO and AEO with a new dimension – content must not only rank but be cited by language models..
- Three engine types: Training-based, search-based, and hybrid models – each type requires different strategies.
- Market development: The share of generative answers is rising rapidly – those who act early secure new touchpoints in digital marketing.
Are you wondering how to make your brand visible in a world where AI models like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google Gemini call the shots? Or do you want to know if these technologies are truly relevant for you?
In this guide, you’ll learn what Generative Engine Optimization means, discover which types of AI engines exist, and get concrete tips on whether and how you should engage with this topic.
-
 Last updated: 10. February 2026SEO Trends 2026: Developing Strategies for the AI Era
Last updated: 10. February 2026SEO Trends 2026: Developing Strategies for the AI Era -
 Last updated: 10. February 2026Understanding Google AI Mode: Overview & Functions
Last updated: 10. February 2026Understanding Google AI Mode: Overview & Functions -
 Last updated: 6. February 2026ChatGPT Search (SearchGPT) Optimization: The Guide
Last updated: 6. February 2026ChatGPT Search (SearchGPT) Optimization: The Guide -
 Last updated: 6. February 2026Large Language Model Optimization (LLMO) Explained
Last updated: 6. February 2026Large Language Model Optimization (LLMO) Explained -
 Last updated: 6. February 2026Answer Engine Optimization (AEO): AI visibility in 2025
Last updated: 6. February 2026Answer Engine Optimization (AEO): AI visibility in 2025
What are Generative AI Engines?
Generative AI Engines (also called Generative Engines or generative AI systems) are systems based on large language models (LLMs) that can independently generate linguistic content from user inputs (prompts) – including answers, texts, recommendations, or problem solutions.
These systems were trained on billions of text fragments from the internet, specialist sources, and structured data. They process natural language, recognize semantic connections, and dynamically combine information to produce context-appropriate outputs.
Examples: ChatGPT (OpenAI), Google Gemini, Claude (Anthropic), Perplexity, Meta LLaMA.
Example Outputs from Generative Engines
An example answer from ChatGPT in the B2B energy sector:
“Who can guarantee me a permanently low industrial electricity price?”

An example answer from Gemini in the B2C sector:
“Which brand produces the best windows in the premium segment?”

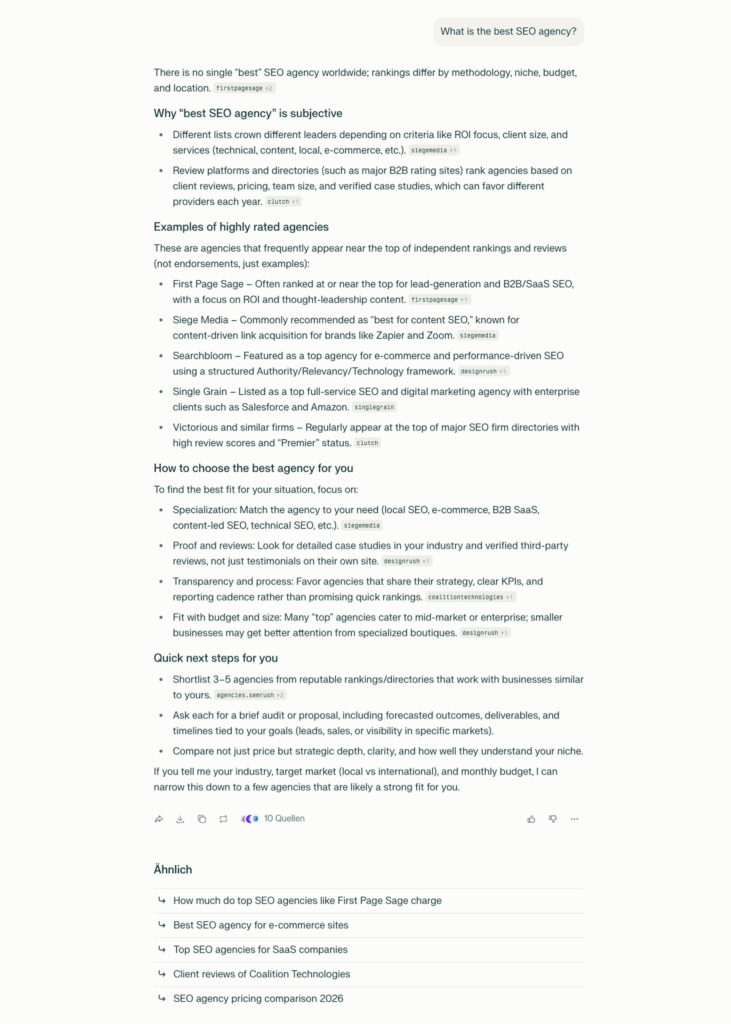
An example answer from Perplexity in the B2B services sector:
“What is the best SEO agency?”
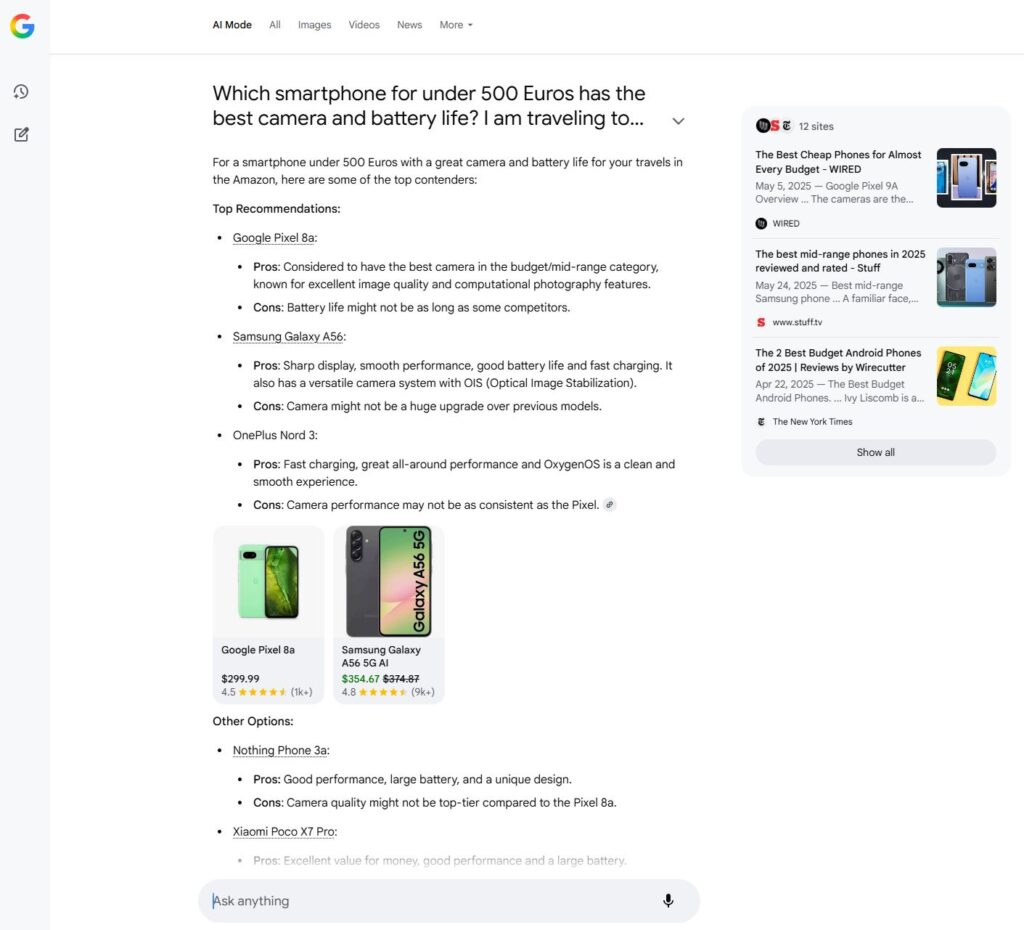
An example answer in Google AI Mode from the B2C sector:
The Three Types of Generative AI Engines
Which types of generative AI engines exist?
Training-Based Systems (e.g., Claude, Llama)
These models are based purely on their training data.
Influence? Only through long-term measures like digital PR and an expanded digital footprint.
Search-Based Systems (e.g., Google AI Overviews, Perplexity)
These engines use real-time indexing of websites.
Here you can score with traditional SEO: ensure your content is among the referenced sources.
Hybrid Systems (e.g., Google Gemini, ChatGPT Search)
Combines training data with current web content.
For example: foundational knowledge comes from the model, current recommendations from the web.
What is Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)?
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO), also called gen AI Engine Optimization, is the strategic process of designing content, brand presence, and digital assets so they are preferentially processed, cited, or directly integrated by generative AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, or Google Gemini.
The goal of GEO is for companies, brands, products, services, or content to become visible in these systems’ outputs – whether as:
- Mention as a brand or solution in answers
- Link or citation in systems with web access
- (Invisible) retrieval during background research by the AI
- Or integration into training data through long-term stable presence on high-quality platforms
GEO Measures
GEO goes beyond traditional SEO because it’s not just about appearing in search results, but becoming directly part of AI systems’ answer logic.
Core measures include:
- Publishing context-rich, structured, unique information on trustworthy sources
- Positioning on platforms actively feeding into LLM training (e.g., Wikipedia, Reddit, top-tier media)
- Building authority through strategic PR, data leadership, and thought leadership.
- Technical and semantic optimization for machine readability
LLM + RAG = Accurate and Reliable
Language models like ChatGPT or Google Gemini sometimes deliver precise answers, sometimes confusing or incorrect information.
The reason is they don’t understand content—they analyze how words relate to each other.
A solution has been found for this:
What is Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)?
RAG improves the quality of AI answers by accessing external sources. This way, the model combines its own knowledge with current information.
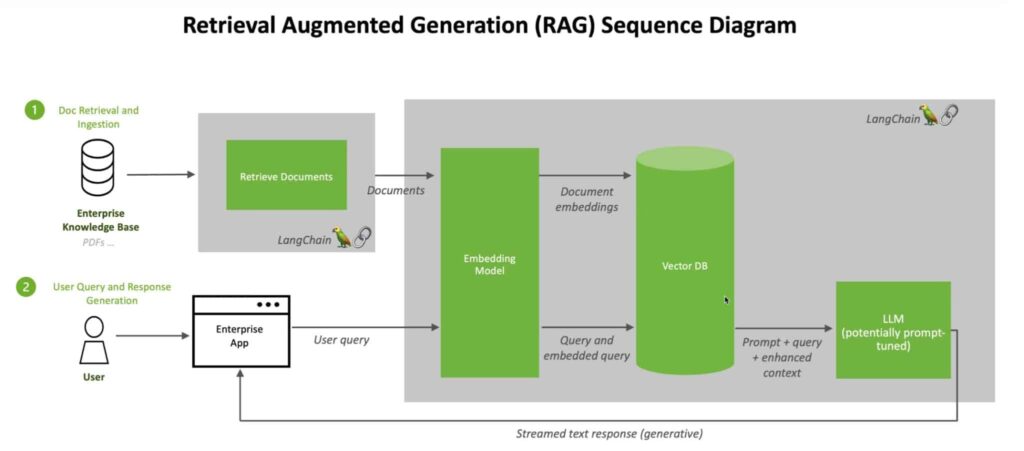
Benefits of RAG:
- Access to current, reliable facts
- Transparency: Users see the sources of answers
This reduces the need to constantly retrain a model and ensures more trustworthy answers.
What RAG Means for You
Systems like ChatGPT and Google Gemini with internet access use RAG to pull current content from search engine indexes.
How it works:
- Internal data: The LLM uses its training knowledge. This is barely influenceable for you.
- External sources: Current content from the web is added. Here you can generate more visibility through SEO.
The result is a curated answer from relevant information and facts that are unique in their combination.
Which Search Engine Indexes Do Different Generative Engines Use?
- ChatGPT = Bing
- Gemini = Google
- Perplexity has its own index
What We Learned from the Claude Leak (Update from May 22, 2025)
The leaked Claude system prompt shows for the first time in detail when a language model like Claude accesses external content at all—and when it doesn’t.
By default, Claude answers from internal model knowledge without triggering a web search. Only when information is either current, multi-dimensional, or outside the training corpus is it actively looked up – and only then is there any chance of source citation.
This means:
For stable, “encyclopedia-like” topics, you typically have no chance of traffic because the model delivers the answer internally and doesn’t cite a source.
Visibility only emerges where the model truly needs external content. It’s crucial to be present in the categories “single_search” (current facts) or “research” (complex tasks)—only there is anything searched, cited, or linked at all. Content must not only be correct and high-quality but so structured, current, or irreplaceable that the model can’t help but reference it.
For GEO, this means: Content must be so specific or current that the model can’t answer it internally or simply rephrase it. This applies, for example, to interactive tools, current market comparisons, continuously updated price lists, study results, or experience reports. Only then is content searched, mentioned, or linked at all.
Does Generative AI Change Search Traffic – Less or More?
Many believe tools like ChatGPT and Perplexity are displacing traditional search engines. In reality, generative AI isn’t changing demand, but the path to the answer. Customers reach their goal faster: fewer clicks, fewer touchpoints, but just as many potential conversions.
Why I believe this is exactly what’s happening:
Traditional search queries were mostly simple, direct, and context-poor—with the result that over 97% of traffic on most websites didn’t convert.
But AI tools like ChatGPT, Google Gemini, AI Overviews, Copilot, and Perplexity open completely new possibilities for more complex questions—ones that couldn’t be answered before.
Instead of simply searching “best laptops 2025,” you ask generative engines:
“Which laptops under $1,500 are best suited for video editing, gaming, and have long battery life?”
Now, through AI-powered chatbots and search engines, a helpful answer can be delivered, curated from many sources.
Generative AI will replace simple, generic search queries—but those were rarely conversion-strong anyway. The question isn’t what falls away, but which search intents are truly valuable for companies.
Years ago, we recommended to our clients to start further down the marketing funnel, as that’s where revenue is generated and everything else could be eaten away by AI.
According to Gartner, search volume via traditional search engines will drop by 25% by 2026. Generative AI is becoming the answer machine and forcing companies to rethink their channel-strategy.
Organic and paid search are vital channels for tech marketers seeking to reach awareness and demand generation goals. Generative AI (GenAI) solutions are becoming substitute answer engines, replacing user queries that previously may have been executed in traditional search engines. This will force companies to rethink their marketing channels strategy as GenAI becomes more embedded across all aspects of the enterprise.
This development has proven “different.”
Search volume has increased. People search more on Google. ChatGPT isn’t replacing Google either; complementary queries are being made (Source: SEMRush).
But clicks are indeed declining significantly.
Current studies – such as from Ahrefs – already show a clear decline in clicks through AI Overviews. With Google AI Mode, a conversation-based search experience, this trend is likely to intensify. The new mode was fully rolled out in the U.S. in May 2025 as a separate tab. Since early October 2025, AI Mode is also available in Europa.
Consumers, but also B2B buyers, suddenly have an AI assistant through ChatGPT, Copilot, and AI Mode – an advisor quickly guiding them through the buying journey. Clicks are no longer the metric, because these platforms aren’t designed for that. They influence purchasing decisions but rarely send a click.
Is attribution dead? Yes, partially, honestly.
People go directly to the website, Google the brand or product, or go to the good old brick-and-mortar store. Attribution is difficult there. Nevertheless, the channel is unavoidable, as this current study from McKinsey shows:
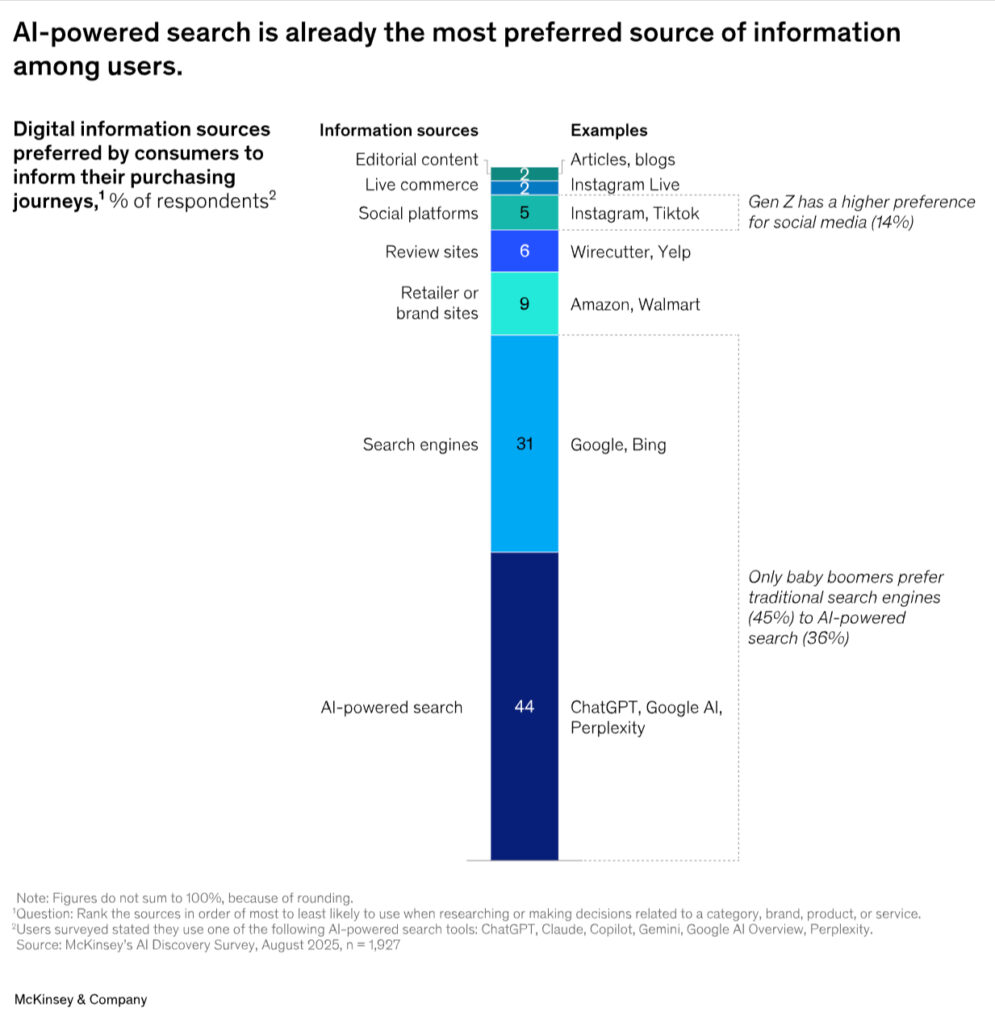
Companies and marketing teams will have to learn that clicks or traffic aren’t valuable marketing-KPIs. For most business models, they never were. Purchasing decisions are increasingly made through AI Search before people land on your own website. This requires complete rethinking.
We’re still relatively at the beginning of this paradigm shift. Nevertheless, we recommend to our clients to thoroughly examine the potential in their industry, even independent of traffic potential. More on this at the end of the guide.
Our Assessment:
- Generative AI changes how people search, not whether they search
- Traditional, short-form search queries (e.g., “best laptops”) are declining, but more complex search dialogues are emerging
- The total number of searches is rising, but they proceed differently: faster, more dialogic, often without a click
- Visibility shifts toward the answer surface—not to the website, but into the model. Those who want to stay relevant must appear in these new answer environments
Should You Optimize Your Brand for Generative Engines?
Yes, because while we’re still at the beginning, this technology is already relevant today:
- Google AI Mode is active in over 200 countries, including Europe
- ChatGPT has over 3.8 billion monthly visits (Source: SimilarWeb).
The importance of Generative Engines is therefore growing rapidly.
Our Budget Allocation Recommendation:
- If your SEO-strategy is already strong, invest an additional 20-25% of your SEO budget in GEO
- If SEO still needs to be expanded, prioritize this area. GEO builds on these results
According to a current analysis by Seer Interactive, there’s a strong correlation (approx. 0.65) between a digital brand’s Google page-1 rankings and mentions in LLMs (Disclaimer: correlation doesn’t imply causation).
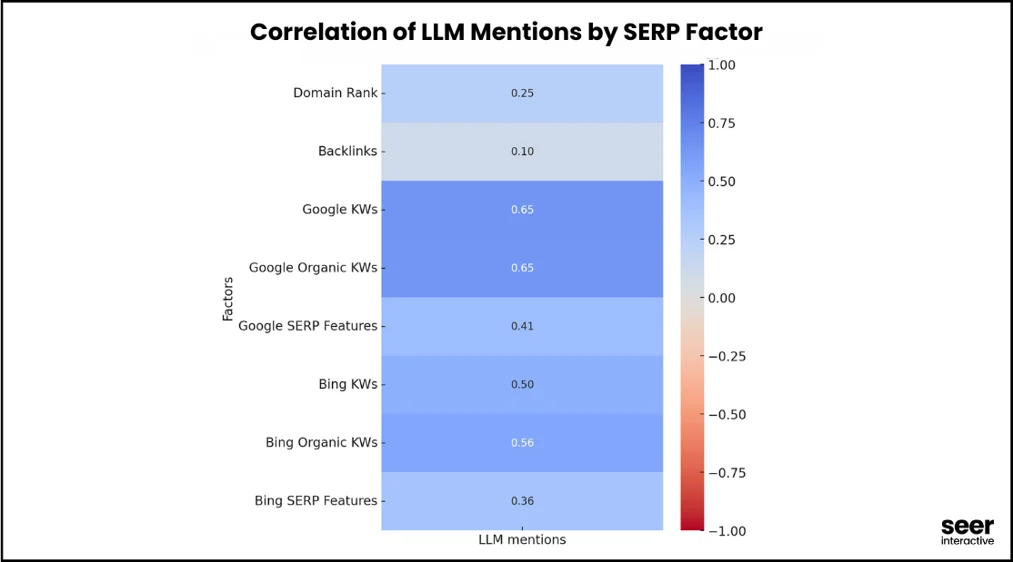
Generative Engines won’t make traditional SEO, content-marketing and digital PR obsolete – rather, these measures are the foundation for success on these AI platforms.
My Personal Perspective:
Generative Engines are a superior interface for accessing information.
The old search systems forced us to make everything as generic as possible and be everything to everyone. That was never good. The new systems will revolve around providing content and information precisely for the target audience at the right time.
How Can You Optimize Your Brand for Generative Engines?
1. What Gets Cited in Your Niche?
The first step requires detailed research and analysis of AI citations and brand mentions in your industry to understand where, how, and why certain brands are highlighted in answers from AI models like ChatGPT, Perplexity, or Google Gemini.
Procedure:
- Industry and topic analysis: Define relevant topics, questions, and objections along the customer journey
- Identification of key players: Analyze important influencers, sources, and competitors
- Successful content formats: Examine content types achieving high citation rates
- Pattern recognition: Identify factors increasing visibility in AI answers
- Action recommendations: Derive actionable high-impact measures
You can conduct a corresponding AI Visibility Audit yourself or book it with us.
2. Why Are These Contents Cited?
In this video, you’ll learn which content is cited by AI search engines and why:
3. How Can Your Brand Be Cited More Frequently?
Typical GEO measures can be roughly divided as follows:
- Content optimization: e.g., format and relevance of answers, optimized page structure.
- Structural adjustments: e.g., improved website-structure, targeted content segmentation.
- External measures: e.g., digital PR, use of knowledge platforms and aggregators and expanding of the digital footprint.
In this video, I’ll show you how to optimize content for AI Overviews or ensure your own website gets cited. All recommendations are also applicable to other generative engines.
Please don’t believe that basic SEO tactics and content optimization are enough. This quote from Tom Critchlow best describes the paradigm shift:
The future of AI-search isn’t about rankings, it’s about recommendations. I think all of the talk about vector embeddings and passage indexation misses the forest for the trees.
Indexation and so on will continue to be important but if you’re not giving the LLM a reason to recommend your page/product/brand then you’re going to get left behind.



Comment