Key Takeaways:
- What is SEO? All measures to improve visibility in organic search—with focus on relevance, authority, and machine readability.
- How do search engines work? Through crawling, indexing, and ranking—supplemented by AI-driven answer systems like AI Overviews.
- What does it include? OnPage optimization, technical SEO, and OffPage factors work together.
- What’s changing? Generative search systems, AI workflows, Search Everywhere Optimization.
- How do you measure success? Visibility for relevant queries, clicks, behavior, conversions.
The search engine is the internet’s gatekeeper – it decides who becomes visible and who disappears into nowhere.
While millions of websites compete for attention daily, only a few land on the first page of search results.
Those who don’t know or ignore the digital gatekeeper’s rules stay outside – no matter how good their offering actually is.
What is Search Engine Optimization (SEO)?
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) refers to all strategic, technical, content-related, and external measures aimed at improving the visibility of websites in the organic results of search engines.
The goal is to provide content so search engines classify it as relevant, trustworthy, and authoritative while optimally fulfilling users’ needs and expectations.
What is SEO simply expressed? It’s the art of capturing existing demand on selected topics through search engines.
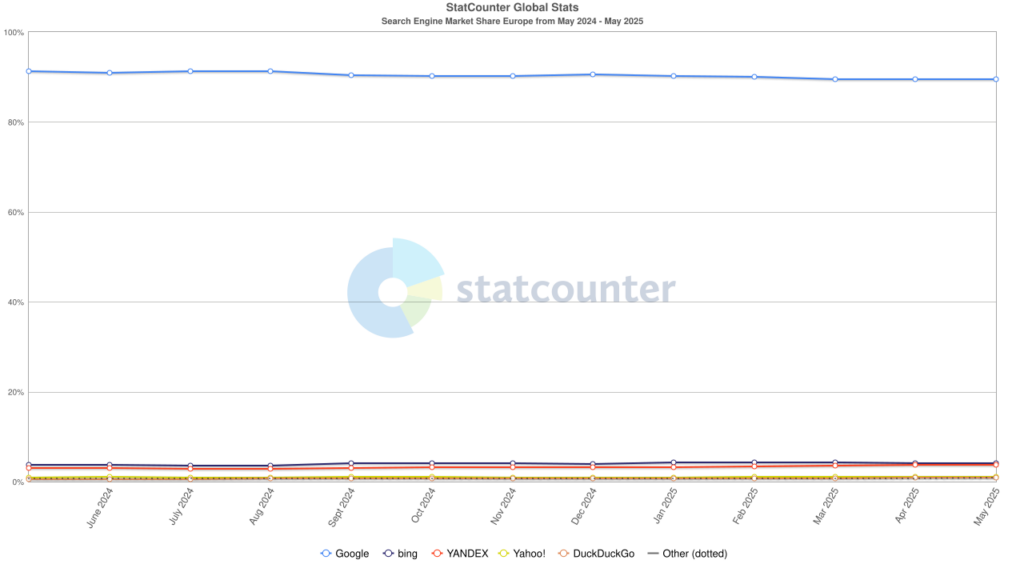
The term derives from “Search Engine Optimization” and currently refers primarily to Google, which has a market share of over 89% in Europe (as of May 2025).
SEO is not a one-time project, but a continuous process. Search engines like Google regularly change their algorithms to deliver the best possible results to users.
Why Is SEO a Central Growth Driver?
SEO remains a crucial growth driver for companies in 2025. Organic search still delivers the largest portion of website traffic and is characterized by high conversion rates.
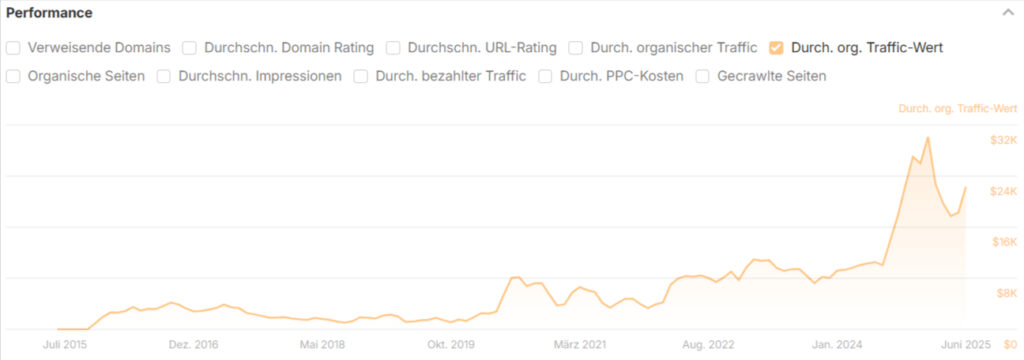
According to current data, “SEO achieves an impressive 748% return on average and can reach up to 1,389% in certain industries, such as real estate.”
Unlike paid ads, there are no direct costs per click, making SEO particularly sustainable. The ROI (Return on Investment) of SEO often surpasses other marketing channels long-term.
With increasing digitalization, search behavior has fundamentally changed. Information is primarily sought through search engines. Those not visible here practically don’t exist for potential customers.
SEO should never be viewed in isolation. You achieve the best results when SEO is strategically combined with other channels like search engine advertising, digitale PR, social media and content marketing.
How Does Search Engine Optimization Work?
- The internet is the library
- Each website is a book
- Each web page is a single book page
- Search engines are the librarian
Crawling, Indexing, Ranking
Crawling: Search engines like Google send out automated bots that discover new content on the web – comparable to a librarian leafing through new books.
Indexing: Discovered pages are thematically categorized and added to the search index – just as a book page is made findable in the library catalog.
Ranking: For a search query, Google decides which books and book pages are best for the question posed – based on relevance, authority, and user experience.
SEO today therefore means: preparing content so it’s not only found and understood, but can also be used as a valuable building block in a system-generated answer – whether in AI Overviews, chatbots, voice assistants, or other generative search experiences.
The new question is no longer just: Will my page be found? But: Will my brand become part of the answer?
Ranking Factors Overview
The most important ranking factors can be divided into three categories:
| Category | Example Factors | Significance |
| Relevance | Search intent match, dwell time, topic coverage | Determines how well your content matches the search query |
| Authority | Backlinks, mentions | Shows Google how trustworthy or credible your page is |
| User Experience | Loading speed, Mobile-First, Core Web Vitals | Evaluates how satisfying your website is |
The algorithm evaluates these factors in combination, not in isolation. High relevance can partially compensate for lower authority and vice versa. The weighting of factors also changes regularly through algorithm updates.
Current Role of AI in Algorithm Development
Artificial intelligence is now a central element in Google’s search technology—not only in ranking but also in the presentation of results. With RankBrain (since 2015), machine learning deployment began, followed by BERT (2019) for contextual language processing and MUM (2021) for multimodal understanding of complex queries.
Since then, Google has significantly developed its AI systems. Today, Google uses highly developed generative models (comparable to GPT-4 or Gemini) to generate AI Overviews – directly compiling answers from trustworthy sources instead of just delivering traditional search results.
For SEO, this means:
- It’s no longer just about rankings of individual pages, but about appearing as a high-quality source in curated answers
- Thematic depth, semantic structure, and professional authority are more important than ever
- Traditional “keyword targeting” recedes – instead, relevance in context, content clarity, trustworthiness, and machine usability count
What Does SEO Deliver?
SEO ensures your content is findable in relevant digital systems—whether traditional search engine, AI-powered search interface, or generative chat interface.
Properly implemented, SEO delivers:
- Visibility in Google & Co.: through rankings, snippets, or AI Overviews
- Citability in systems like ChatGPT (with search), AI Mode or Perplexity: where answers are generated from external sources
- Long-term presence in training data: through content on linked platforms, in media, or forums
- Reach along the entire customer journey: from first contact to conversion
- Qualified access without direct click costs: instead of just buying traffic
- Digital visibility without campaign dependency: SEO scales permanently
In short: SEO doesn’t just get you into search results, but into answers—everywhere people search today.
There are three relevant classes of search systems that SEO influences today:
- Traditional search engines – e.g., Google, Bing
→ deliver links and increasingly AI-generated answers - AI-powered search interfaces – e.g., ChatGPT with web browsing, Perplexity, You.com
→ generate answers, use sources, show citations, link - Generative chatbots without live search – e.g., GPT-4 without browser, Claude without web access
→ access training data → visibility requires getting into this data
Which Areas Fall Under SEO?
Search engine optimization encompasses various sub-areas that must work together to achieve sustainable success. An effective SEO strategy considers all three main areas: OnPage factors, OffPage factors, and technical optimization.
1. OnPage Factors
OnPage optimization includes all measures on your own website that improve relevance, usability, and machine readability. It forms the technical and content foundation of every effective SEO strategy – and determines whether content can be properly understood and used by search systems.
Content That Truly Helps
High-quality content remains central – but not just regarding length or keywords, but clarity, depth, and structural comprehensibility. Google prefers content that:
- Answers concrete questions
- Is thematically clearly demarcated
- Appears content-reliable (authorship, sources, experience, expertise)
- Is suitable as an answer building block for AI-generated search formats
Semantic Structure Instead of Keyword Stuffing
Relevant keywords remain important—but not as a checklist. Today counts:
- Semantic classification instead of keyword density
- Clean heading structure (H1–H4) with real information value
- Entity assignment (topics, brands, concepts)
Optimizing Title-Tags and Meta-Descriptions remains important – especially to improve click-through rates (CTR) in traditional SERPs .
Internal Linking & Structured Data
A logically constructed, thematically focused internal linking structure helps both users and search engines understand connections and build authority. Topic clusters and cornerstone pages continue to gain importance.
With structured data (Schema.org), you signal what your page is about—for products, people, FAQs, or organizations. Today this is not only helpful for rich snippets but essential for AI Overviews, chatbots, and other new search formats that evaluate content mechanically.
2. OffPage Factors
OffPage optimization encompasses all measures outside your own website aimed at strengthening reputation, trustworthiness, and thematic authority on the web. The central lever remains the quality and relevance of external signals pointing to your content.
Backlinks Remain Essential
Backlinks from thematically appropriate, authoritative sources remain one of the strongest signals for Google’s evaluation of expertise and authority. What counts is not just quantity, but especially context, placement, and the relevance of linking content.
Brand Strength and Entity Signals Gain Importance
Google increasingly recognizes unlinked brand mentions and uses them in entity processing. These “implicit links” strengthen your presence in the semantic web – especially when your brand is mentioned in trustworthy publications. In AI Overviews, for example, content from known, established sources is preferentially cited.
Local Citations for Local SEO
For local businesses, consistency of NAP data (Name, Address, Phone) across business directories, review portals, and map platforms remains an important ranking factor. These local signals particularly influence visibility in Google Maps and Local Pack search.
Social Signals: Visibility, Not Ranking
Likes, shares, and comments on social networks have no direct influence on ranking – but they can generate reach, reach relevant audiences, and thus indirectly contribute to links and brand building.
3. Technical Optimization
Technical SEO forms the foundation of every successful search strategy. It ensures search engines can efficiently crawl, index, and correctly interpret content.
Crawling and Structure
A clean website-structure with clear internal linking helps both bots and users quickly find relevant content. Technical barriers like faulty redirects, broken links, or blocked resources should be avoided.
Mobile-First and Performance
Since introduction of the Mobile-First Index, Google evaluates websites primarily based on their mobile version. Content must be fully and performantly available on mobile. Loading speed also influences ranking – not directly as a penalty factor, but as a quality feature in competition.
Core Web Vitals
The Core Web Vitals have measured aspects of user experience since 2021: loading speed (Largest Contentful Paint, LCP), visual stability (Cumulative Layout Shift, CLS), and responsiveness (First Input Delay, FID). The previous FID was replaced by Interaction to Next Paint (INP) in 2024. These metrics are secondary ranking factors and act primarily as tiebreakers with equivalent content.
What Are Current SEO Trends?
The SEO landscape is constantly evolving. In 2025, these trends particularly shape search engine optimization:
1. Google AI Overviews
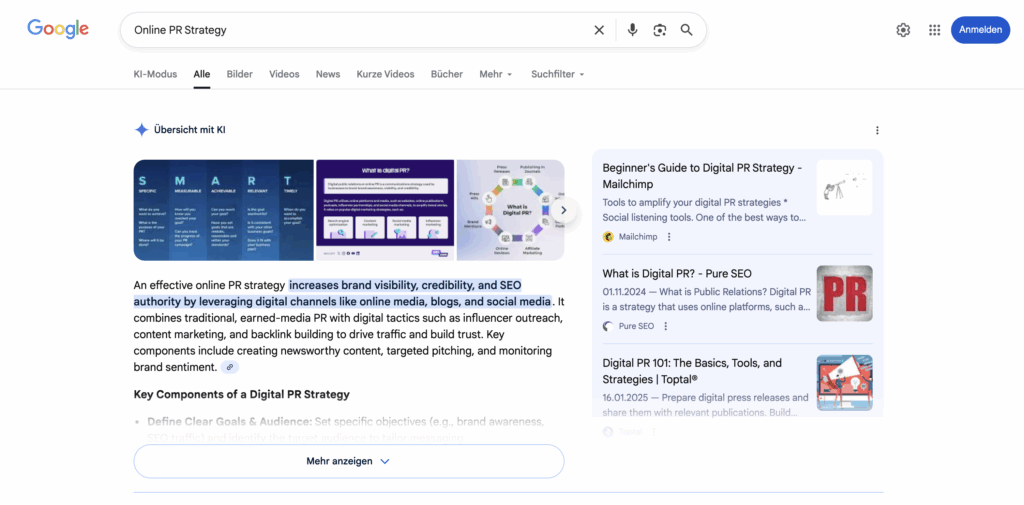
Google AI Overviews (formerly SGE – Search Generative Experience) are revolutionizing search result pages. These AI-generated summaries appear above traditional search results and answer user queries directly in the SERPs. According to the Ahrefs-study, “54.61% of all search queries now show AI overviews, leading to a decline in clicks on organic results by up to 34.5% for position 1.”
For SEOs, this means a new challenge: not only ranking on page 1, but also being cited as a source in these AI overviews. Websites with clear structure, precise answers, and high authority have the best chances here.
- Structured content more important than ever: Clear answers, lists, and tables are preferred
- Source citation as new traffic factor: Websites named as sources receive higher click rates
- E-E-A-T becomes crucial: Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness determine which sources are cited
- Topic coverage instead of keyword focus: Comprehensive content treating a topic holistically
- Update frequency: Regularly updated content has better chances of appearing in AI Overviews
2. Google AI Mode
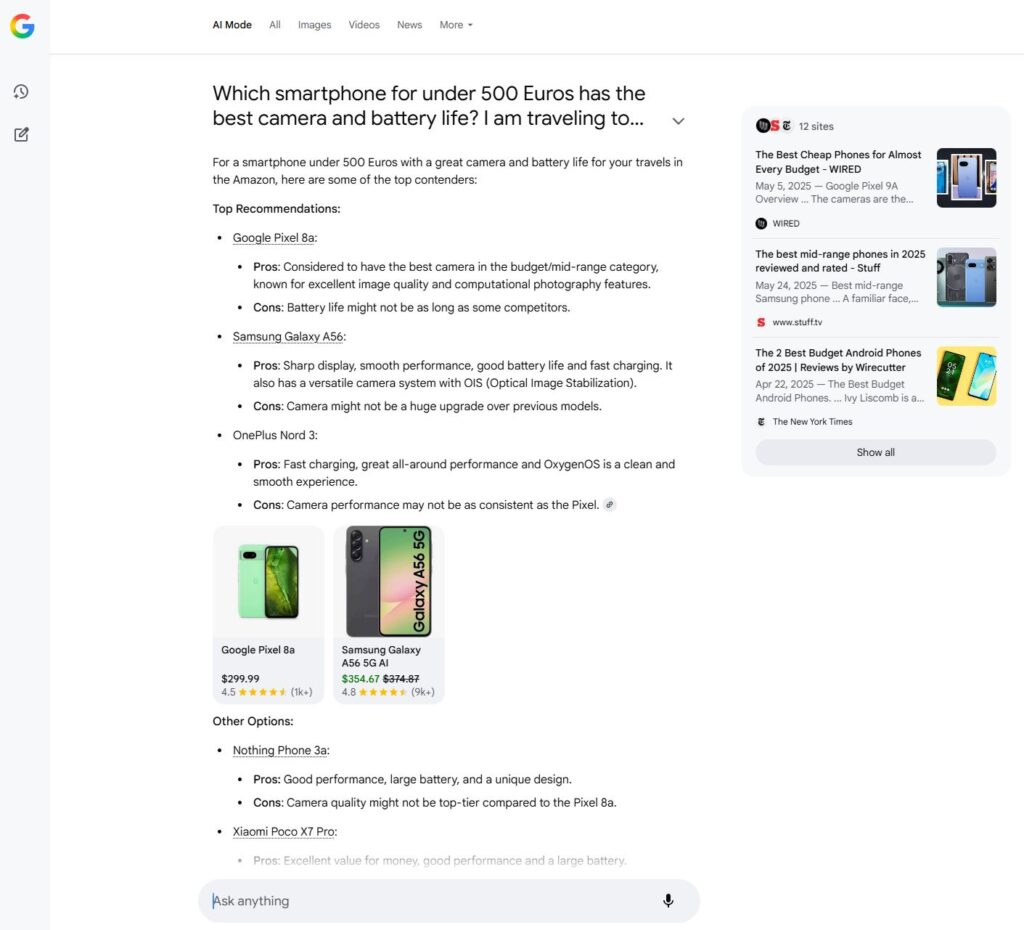
Google AI Mode is a new mode in Google Search based on a ChatGPT-like interface. Users no longer get their search results as a classic link list, but as a conversational answer compiled by Google’s AI.mengestellt wird.
Instead of just showing individual web pages, the AI analyzes various sources and creates its own coherent answer from them – often with context, explanations, and follow-up questions. Traditional search remains, but in AI Mode, the answer, not the document, is central.
3. Search Everywhere Optimization
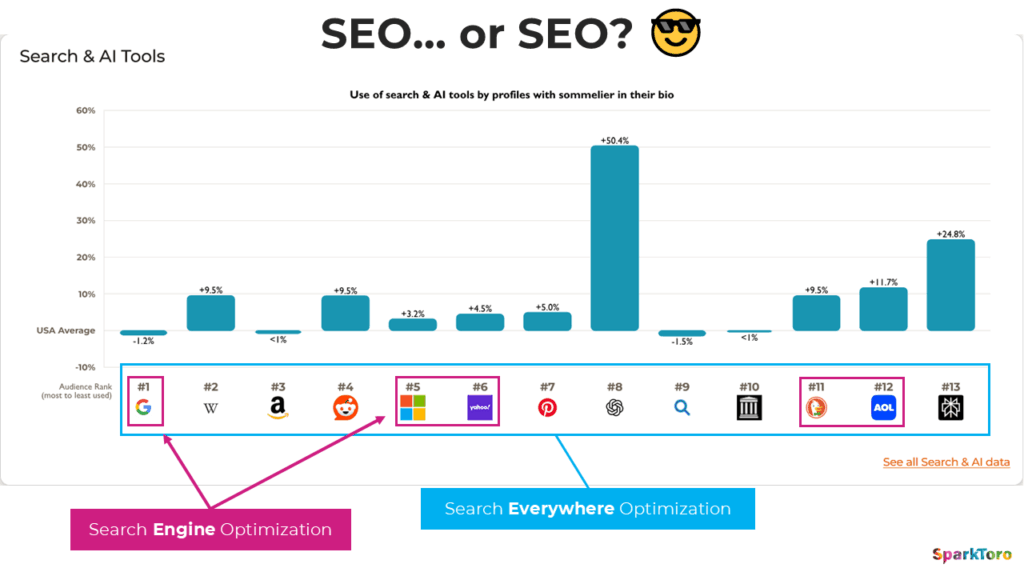
SEO is evolving from “Search Engine Optimization” to “Search Everywhere Optimization.” Users no longer search only on Google, but also on social platforms like TikTok, Instagram, and YouTube, through voice assistants like Alexa and Google Assistant, in vertical search engines like Amazon for products, and through AI chatbots like ChatGPT and Claude.
A future-proof SEO strategy considers this fragmented search landscape and optimizes content cross-platform. The key lies in creating high-quality, versatile content that can be adapted for different platforms and formats.
4. AI Agents and AI Content Workflows
More and more SEO teams are deploying specialized AI-agents and automated workflows to handle repeatable tasks like keyword research, content briefs, or drafts more efficiently. These agents work with clearly defined roles and goals – similar to digital team members.
Instead of just “writing texts with ChatGPT,” entire workflows are developed that map research, conception, creation, and quality assurance in modular steps—often aligned with specific topic clusters, brand guidelines, or search intents.
This saves time, increases consistency, and makes SEO work scalable without giving up strategic control.
How Can You Measure SEO Success?
SEO success no longer shows only in rankings or visibility values, but in real impact. Those who operate SEO professionally today measure impact along the entire customer journey – from visibility to conversion.
1. Impact Instead of Rankings
Traditional keyword rankings are no longer sufficient as sole success indicators. Much more relevant is the question:
Are you visible for the right search queries – and do you manage to convince users?
For this, you analyze:
- Thematic visibility: How well does your content cover your target audience’s search intents?
- Click-through rates (CTR): Are you not only found in search results but also clicked?
- Engagement signals: How long do users stay on the page? Do they scroll, click further, convert?
Particularly relevant in the context of AI Overviews and AI Mode: Are you cited or used as a trustworthy source? This shows whether your content also has “answer quality” for Google.
2. Measuring with Substance: Tools & Data Sources
Google Search Console and GA4 remain the foundation. They show which search queries find you, how users behave, and which pages create impact.
For deeper analyses, professional teams rely on:
- Logfile analyses: Show how Googlebot actually crawls your pages—not how tools simulate it
- Event and conversion tracking: Not just counting clicks, but what happens afterward—lead, purchase, inquiry
- Dashboards (e.g., Looker Studio or BigQuery + BI tool): To connect SEO data with business goals and make them visible across teams
Today you get keyword and competitive data from Ahrefs or SEMrush, not from visibility indices without real business reference.
3. Business Impact: Conversions and ROI
SEO is not an end in itself. What’s decisive is the contribution to business goals:
- How many qualified leads does SEO bring?
- How much revenue is generated attributed to SEO?
- What’s the Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) of users acquired through SEO?
A realistic ROI requires clean attribution. Ideally, you combine data from CRM, web analytics, and SEO monitoring – so you don’t just know what’s visible, but what contributes to business goals.
How Long Does SEO Take?
SEO is not a short-term measure, but a strategic process. Results build up gradually – depending on competition, internal implementation speed, and existing substance.
Realistic Timeframes for SEO Effects:
| Phase | Timeframe | What happens during this time? |
| First signals | 3–6 months | Indexing, crawling improvement, first keyword movements |
| Tangible results | 6–12 months | More visibility for relevant queries, first leads and conversions |
| Strategic impact | 12–24 months | Building thematic authority, sustainable traffic growth |
These timeframes aren’t rigid – they depend heavily on factors like domain reputation, technical condition, competition, content focus, and internal resources.
Today applies: Those who work efficiently and focus on quality, clarity, and user intent can see first effects faster—especially in long-tail and AI-generated search formats.
What Does SEO Cost?
Costs depend on whether you optimize selectively or understand SEO as a growth channel. It’s not just about text – but technical excellence, strategic clarity, and editorial quality.
| Service | Typical Cost Range (2025) | Notes |
| SEO Audit & Strategy | 8.000–15.000 € (one-time) | Solid analysis, potential, roadmap |
| Monthly Retainer | 3.000–20.000 €+ | Ongoing consulting, implementation, reporting |
| Project-Based Implementation | 10.000–50.000 €+ | Relaunches, new content hubs, AI workflows |
| In-house SEO Team | 60.000–100.000 €+ p.a. per person | For building, steering, and internal impact chain |
SEO isn’t “text and a few meta tags,” but a cross-functional lever—between editorial, development, UX, data, and management. Those who want to grow sustainably need a strong setup – not a package deal.
Good SEO work isn’t a cost block, but a growth driver. It pays for itself through organic new customer acquisition, reduced dependence on paid media, and better user experience.
What Are Your Next Steps?
SEO in 2025 isn’t a to-do list, but a strategic decision. It’s no longer just about optimizing pages – but how you establish yourself as a reliable source in a fragmented, AI-driven web. Therefore:
1. Position SEO as part of your growth strategy.
Not as a project. Not as a one-time measure. SEO is a systemic lever for visibility, trust, and digital impact. This requires clarity, resources – and internal commitment.
2. Understand how modern search works.
Google no longer delivers link lists, but answers. Whether AI Overviews, chatbots, or conversational search: only those who are machine-readable, indispensable, and current become part of these new answer formats.
3. Don’t start with tools, but with questions.
- Where is our brand visible today – and where not?
- What do we want to be perceived as a trustworthy source for?
- Which topics do we credibly cover – and which (not yet)?
These questions are more important than any visibility index.
4. Think in systems, not tactics.
Successful SEO teams combine strategy, editorial, UX, data, PR, and tech in an integrated setup. They work with AI, but not blindly. They analyze, test, prioritize—and implement consistently.
5. Don’t be blinded by short-term results.
SEO isn’t a performance marketing channel with daily evaluation. It’s an investment in digital brand building – and this pays off.
If you want clarity on where you currently stand and need a roadmap for how to position yourself: We’ll help you work out exactly that.




Comment